Jaw Crusher

What is Jaw Crusher?
Jaw crusher is composed of two jaw plates, the moving jaw and the static jaw, which simulate the movement of the two jaws of animals to complete the material crushing operation. It is widely used in the crushing of various ores and bulk materials in the mining and smelting, building materials, highways, railways, water conservancy and chemical industries.

Working Principle of Jaw Crusher
The jaw crusher uses the compression between the two jaw plates to crush the material. The movable jaw plate makes periodic swinging motion, and the material is crushed by the squeezing, bending and friction between the movable and fixed jaw plates.
Main Components of Jaw Crusher
Jaw Crusher Types
How to Choose the Right Jaw Crusher?
Choosing the right jaw crusher is crucial for optimizing material processing efficiency and achieving the desired crushing results. With various models and specifications available, selecting the best jaw crusher requires careful consideration of factors such as material type, production capacity, and operational requirements. A well-chosen crusher ensures higher productivity, lower operational costs, and long-term reliability. This article explores key factors to consider when selecting a jaw crusher, helping industries make informed decisions.
Understanding the Material to Be Crushed
The first step in choosing the right jaw crusher is understanding the type of material it will process. Different crushers are designed to handle varying hardness levels, from soft limestone to hard granite or abrasive ores. The material's compressive strength, moisture content, and abrasiveness affect the choice of jaw plate material and crusher configuration. Selecting a crusher suited for the specific material type ensures efficient crushing and minimal wear on components.
Determining the Required Crushing Capacity
Production capacity is a critical factor when selecting a jaw crusher. The crusher must be capable of handling the required tonnage per hour to meet production goals. Overestimating capacity may lead to unnecessary costs, while underestimating it can cause operational bottlenecks. Evaluating the feed size and output size requirements helps in determining the right jaw crusher model to maximize efficiency.
Considering the Feed and Discharge Sizes
The size of the feed material and the desired output size play a significant role in selecting a jaw crusher. The crusher’s feed opening should be large enough to accommodate the maximum material size without causing blockages. Additionally, the required final product size determines the settings of the crusher’s discharge opening. Properly matching the feed and discharge sizes ensures smooth operation and optimal material reduction.
Evaluating Power and Energy Efficiency
Jaw crushers vary in power requirements depending on their size and design. Selecting a crusher with an appropriate power rating ensures efficient operation without excessive energy consumption. Energy-efficient models help reduce operating costs and environmental impact while maintaining high productivity. Crushers with modern power-saving features can enhance performance and long-term cost savings.
Assessing Durability and Maintenance Needs
Durability and ease of maintenance are key considerations when choosing a jaw crusher. A robust frame, high-quality jaw plates, and wear-resistant components contribute to the crusher’s longevity. Additionally, crushers with accessible maintenance points and user-friendly design simplify repairs and reduce downtime. Regular maintenance schedules should be considered to ensure the crusher operates at peak efficiency.
Considering Mobility and Installation Requirements
Depending on the application, a stationary or mobile jaw crusher may be required. Mobile crushers offer greater flexibility for on-site operations, making them ideal for construction and mining projects requiring frequent relocation. On the other hand, stationary crushers are more suitable for high-capacity, long-term crushing operations. Installation requirements, including space constraints and foundation support, should also be evaluated before making a final selection.
Comparing Different Jaw Crusher Models
Manufacturers offer various jaw crusher models, each designed for specific applications. Comparing models based on specifications, features, and price helps in selecting the most suitable crusher. Some advanced models come with hydraulic adjustment systems, automation, and intelligent monitoring capabilities, enhancing operational efficiency and ease of use.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer and Supplier
The reputation and reliability of the manufacturer or supplier are essential when purchasing a jaw crusher. Established manufacturers provide high-quality equipment, reliable after-sales support, and comprehensive warranties. Working with a trusted supplier ensures that the crusher meets performance expectations and comes with the necessary technical support.
Making the Final Decision
Choosing the right jaw crusher requires balancing multiple factors, including material type, capacity, efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Conducting thorough research, consulting with industry experts, and assessing long-term operational needs can help make an informed decision. A well-chosen jaw crusher enhances productivity, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures smooth material processing for years to come.


Applications of Jaw Crusher
The jaw crusher is one of the most essential pieces of equipment in various industries, known for its ability to break down large, hard materials into smaller, manageable sizes. From mining to construction and even recycling, its versatility makes it a crucial tool for different applications. The simplicity of its design, combined with its efficiency and durability, allows it to be used in a wide range of material processing operations. This article explores the diverse applications of jaw crushers and their significance in different industries.
Mining and Quarrying
One of the primary applications of jaw crushers is in the mining and quarrying industry. These machines are widely used to crush hard and abrasive materials such as granite, basalt, and ores. In mining, jaw crushers serve as the first stage of material reduction, breaking down large chunks of rock before they are further processed by secondary crushers or milling machines. Their ability to handle high compressive strength materials makes them ideal for extracting valuable minerals efficiently.
Construction and Demolition
Jaw crushers play a critical role in the construction industry, particularly in the demolition and recycling sectors. When old buildings, roads, or bridges are torn down, large amounts of concrete, bricks, and asphalt need to be processed. A jaw crusher can break down these materials into reusable aggregates, reducing construction waste and promoting sustainable building practices. This not only lowers costs for construction companies but also contributes to environmental conservation by minimizing landfill use.
Road and Infrastructure Development
For large-scale infrastructure projects, such as highways, railways, and bridges, a steady supply of crushed stone and gravel is essential. Jaw crushers are used to produce high-quality aggregates that serve as the foundation for these structures. Their ability to crush a wide variety of raw materials ensures that contractors get consistent, durable materials needed for road bases, concrete production, and other construction applications.
Recycling and Waste Management
As sustainability becomes a growing concern, jaw crushers are increasingly used in recycling applications. These machines can process construction and industrial waste, including concrete, bricks, and scrap metal, turning them into valuable materials for reuse. Many recycling plants utilize jaw crushers to reduce waste volume and recover materials that would otherwise be discarded. This not only saves costs for businesses but also supports circular economy initiatives by reducing the demand for virgin raw materials.
Industrial and Manufacturing Applications
Beyond mining and construction, jaw crushers are also used in various industrial applications. In cement production, for example, raw materials like limestone and clay need to be crushed before they are processed into cement. Similarly, in metallurgy and chemical industries, jaw crushers help break down raw materials required for different manufacturing processes. Their efficiency and ability to handle different materials make them valuable assets in many industrial operations.
Agriculture and Rock Processing
Although not as commonly discussed, jaw crushers also find applications in agriculture. Some farmers and agricultural businesses use them to crush rocks and minerals that are later used to improve soil quality. Crushed stone can help in soil stabilization, erosion control, and even fertilizer production. This niche application highlights the jaw crusher's adaptability beyond traditional industries.
The Backbone of Material Processing
Whether in large-scale mining operations or small recycling plants, jaw crushers continue to be an essential part of material processing. Their ability to efficiently break down hard materials, coupled with their durability and low maintenance requirements, makes them invaluable in numerous industries. As technology advances, jaw crushers are likely to become even more efficient, further expanding their range of applications.
Maintenance of Jaw Crushers
Jaw crushers are essential machines in the mining, construction, and aggregate industries, known for their durability and efficiency in breaking down large materials into manageable sizes. However, to ensure optimal performance and longevity, regular maintenance is crucial. Proper upkeep not only enhances the efficiency of the crusher but also minimizes unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Understanding key maintenance practices can help operators maximize the lifespan and productivity of their jaw crushers.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance is vital for keeping a jaw crusher in peak working condition. Continuous exposure to high loads and abrasive materials can cause wear and tear on critical components. Regular inspections and servicing help identify potential issues early, preventing major failures that could result in prolonged downtime and increased operational costs.
Daily and Weekly Inspections
Performing daily and weekly inspections ensures that minor issues are detected before they become serious problems. Operators should check for loose bolts, excessive vibrations, unusual noises, and any signs of wear on key components such as jaw plates, bearings, and toggles. Monitoring oil levels and ensuring proper lubrication are also essential for smooth operation.
Lubrication and Bearing Maintenance
Proper lubrication is one of the most critical aspects of jaw crusher maintenance. Bearings and other moving parts require regular greasing to reduce friction and prevent overheating. Using the right type and quantity of lubricant ensures smooth operation and extends the lifespan of the crusher components. Additionally, operators should monitor the condition of bearings and replace them if signs of wear or damage appear.
Jaw Plate Wear and Replacement
Jaw plates experience constant pressure and impact, leading to gradual wear. Uneven or excessive wear can affect crushing efficiency and increase power consumption. Regularly inspecting jaw plates and flipping or replacing them when necessary helps maintain consistent performance. Using high-quality replacement jaw plates also enhances durability and reduces maintenance costs.
Checking and Adjusting the Discharge Setting
The discharge setting determines the final product size and must be adjusted periodically to maintain uniform output. Over time, jaw plates and toggles may shift, affecting the gap between the crushing surfaces. Operators should routinely measure and adjust the setting to ensure optimal particle size and efficient operation.
Clearing Blockages and Preventing Overloading
Material blockages can occur due to oversized feed, moisture content, or uneven feeding. Regularly clearing blockages and ensuring a steady feed rate prevent unnecessary strain on the crusher. Overloading can also cause damage to the machine, so operators should monitor material input and avoid feeding excessive amounts at once.
Inspecting the Toggle Plate and Springs
The toggle plate plays a crucial role in the functioning of a jaw crusher by acting as a safety mechanism in case of overloading. If a toggle plate breaks or becomes excessively worn, it must be replaced immediately to avoid operational failures. Similarly, tension springs should be checked regularly to ensure proper tension and alignment.
Monitoring Electrical Components
The electrical system of a jaw crusher, including the motor, wiring, and control panel, should be routinely inspected. Loose connections, overheating, and worn-out electrical components can cause operational failures. Regular maintenance of the electrical system enhances safety and ensures smooth machine operation.
Keeping the Work Area Clean
A clean and organized work environment contributes to better maintenance practices. Dust, dirt, and debris should be regularly removed from the crusher and surrounding area to prevent contamination and potential damage to machine components. Keeping the crusher clean reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns and enhances operational efficiency.
Preventive vs. Reactive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance focuses on scheduled inspections, lubrication, and part replacements before failures occur, whereas reactive maintenance involves repairing breakdowns after they happen. Adopting a preventive maintenance strategy minimizes downtime, reduces repair costs, and extends the overall lifespan of the jaw crusher.
Enhancing Machine Longevity and Performance
Consistent maintenance practices ensure that jaw crushers operate efficiently and reliably over the long term. By following scheduled inspections, proper lubrication routines, and timely part replacements, operators can minimize downtime, reduce operating costs, and maximize productivity. Investing time and effort in regular maintenance is essential for achieving optimal performance and prolonging the service life of jaw crusher machines.

Stone Crusher Types

Jaw Crusher
Compressive Crushing: Utilizes compressive force generated by a reciprocating motion between a fixed jaw plate and a movable jaw plate. The material is crushed by progressive compression as it moves downward through the crushing chamber.
Learn more >>

Cone Crusher
Employs interparticle crushing (also called layer compression), where rocks are crushed between a rotating mantle and a concave liner. The eccentric gyratory motion of the mantle creates a compressive force field, inducing fractures along grain boundaries.
Learn more >>
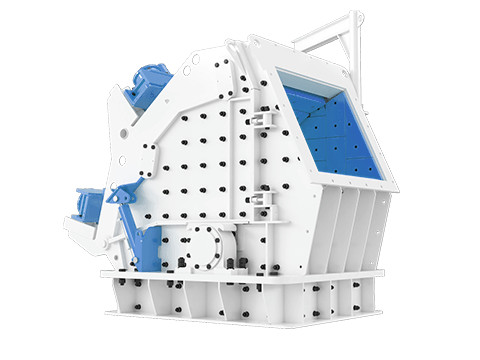
Impact Crusher
Dynamic Impact Crushing: Relies on kinetic energy transfer via high-speed rotors equipped with blow bars or hammers. Material is shattered by direct impact against rotating components or stationary anvils, with secondary fragmentation occurring through particle-on-particle collisions.
Learn more >>

Roll Crusher
Shear-Compression Crushing: Applies shear-compression forces between counter-rotating rolls with textured or smooth surfaces. Material is drawn into the gap (nip angle) and fragmented via tensile failure or surface abrasion.
Learn more >>
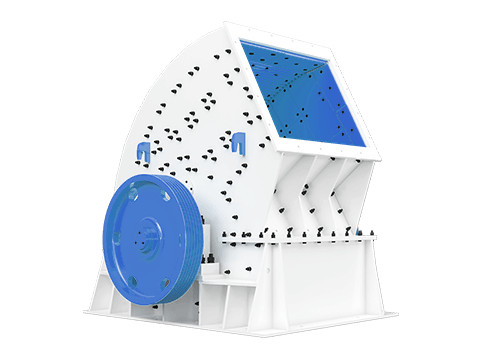
Hammer Crusher
Dynamic Impact with Grinding: Combines high-velocity hammer strikes (rotating hammers on a horizontal shaft) with material grinding against breaker plates or screens. Fragmentation occurs through impact, attrition, and shear.
Learn more >>
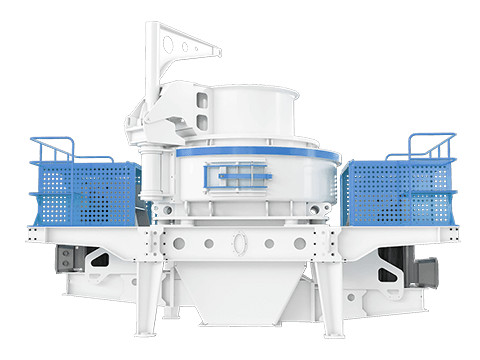
VSI Crusher
Centrifugal Acceleration Crushing: Accelerates material through a high-speed rotor (up to 70 m/s) and projects it against a stationary anvil or rock-lined chamber, exploiting centrifugal force and interparticle collision for fragmentation.
Learn more >>

Gyratory Crusher
Conical Compression Crushing: Operates via a conical head gyrating within a concave bowl, generating progressive compression as material moves downward. Combines elements of jaw and cone crushers for ultra-high-capacity primary crushing.
Learn more >>

Fine Crusher
Fine Crusher is engineered for reliable and stable operation, making it an ideal choice for fine crushing applications across various industries.
Learn more >>

Mobile Crusher
The Mobile Crusher is designed to operate as a primary or secondary unit, making it a versatile choice for various applications.
Learn more >>
